From the Statistics in Medicine special issue on the 25th Annual Conference of the International Society for Clinical Biostatistics, Prof Margaret S. Pepe from University of Washington Dept of Biostatistics and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center's article "Evaluating technologies for classification and prediction in medicine".
To begin with, Prof Pepe points to the CONSORT statement, which in essence gives guidelines for the design, analysis, and reporting of randomized clinical trials of therapeutics. She notes the Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy (STARD) initiative which has arisen to specify analogous guidelines for medical diagnostics.
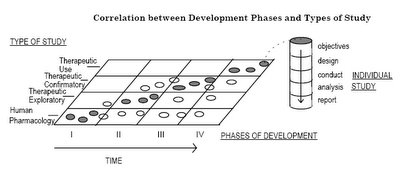
Prof Pepe proposes that the structured investigation of therapeutics into the canonical 4 phases can also be adapted for the investigation of medical diagnostics.
Prof Pepe proposes a 5-phase approach. For each phase she identifies the major objective and the best study design to achieve these goals.
- Preclinical exploratory: to identify promising directions by convenience sample case-control studies
- Clinical assay and validation: to determine if a lcinical assay detects established disease by population-based case-control studies
- Retrospective screening: to determin if the biomarker detects disease before if becomes clinical, and to define a "screen positive" rule, by nested case-control studies
- Prospective screening: to determine the extent and characteristics of disease detected by the test and to identify the false referral rate, by cross-sectional studies
- Cancer control: to aseess the impact of screening on reducing the burden of disease on the population, by--ideally--randomizaed trial
Prof Pepe also identifies a number of interesting statistical issues that apply distinctly to medical diagnostics. Will review.
Technorati Tags:
Medicine / Statistics / Medical diagnostics / Margaret S. Pepe / International Committee of Harmonization




No comments:
Post a Comment